Welcome to Electronic Security System Awareness
As an employee working with electronic security systems daily, you play a crucial role in maintaining organizational security. This course will equip you with the essential knowledge and skills needed to interact safely and effectively with access control, CCTV, alarm systems, and visitor management protocols.
Who This Course Is For
- Front desk personnel
- Security officers
- Administrative staff
- General employees with security system access
- New hires requiring security orientation
What You'll Achieve
By completing this course, you'll confidently and safely operate basic electronic security systems, understand your role in maintaining security protocols, and know how to respond appropriately to various security situations.
Course Outline
- Module 1: Electronic Security System Overview
- Module 2: Access Control & CCTV Awareness
- Module 3: Alarm Systems & Visitor Management
Understanding Electronic Security Systems
Electronic security systems form the technological backbone of modern workplace protection, providing automated, continuous monitoring and access control.
Access Control Systems
Manage who can enter specific areas and when using credentials like key cards, biometrics, or PIN codes; keep detailed logs of entry attempts.
CCTV Systems
Provide visual monitoring and recording with real-time oversight and incident review to enhance awareness.
Alarm Systems
Detect unauthorized access, hazards, or emergencies, triggering alerts and coordinated responses.
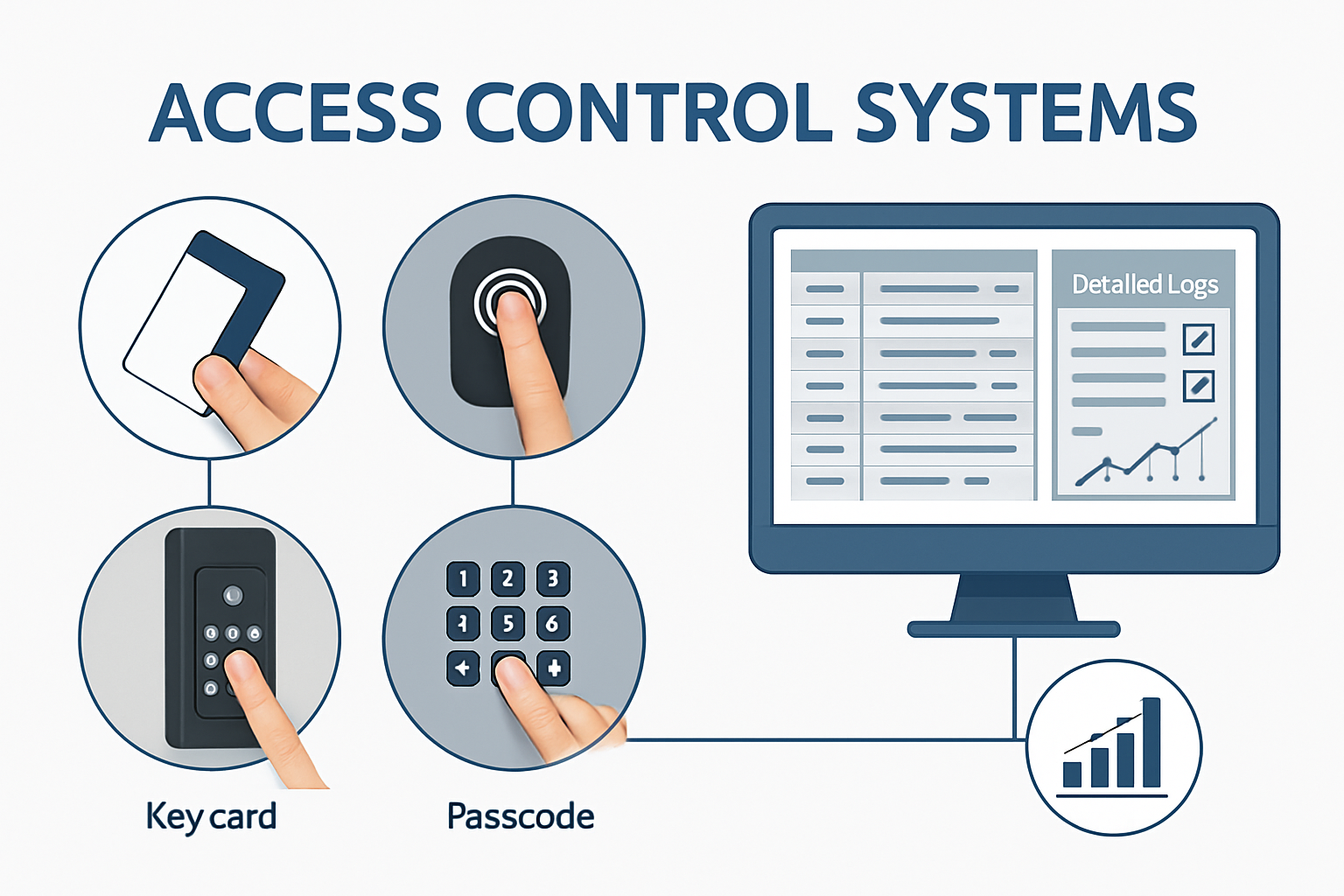
Access Control System
Think of access control like a smart doorman for your building. Only people with the right “key” — a card, fingerprint, or PIN — can open certain doors. Every tap is recorded so we know who entered and when. If a key is lost, it can be turned off so it no longer works. This helps keep the wrong people out and protects areas that need extra care.
- Always use your own badge or code — never share it.
- Wait for doors to close behind you; don’t hold them for strangers.
- If your card is lost or damaged, report it right away.

CCTV Systems
CCTV is like having respectful, always‑on eyes in important areas. Cameras help you and security teams see what’s happening in entrances, lobbies, corridors, parking areas, and other shared spaces. If something goes wrong, recorded video helps explain what happened. Private spaces aren’t monitored.
- Be aware you may be recorded in public/common areas.
- Report camera damage, blockage, or unusual behavior.
- Don’t tamper with cameras or obscure their view.
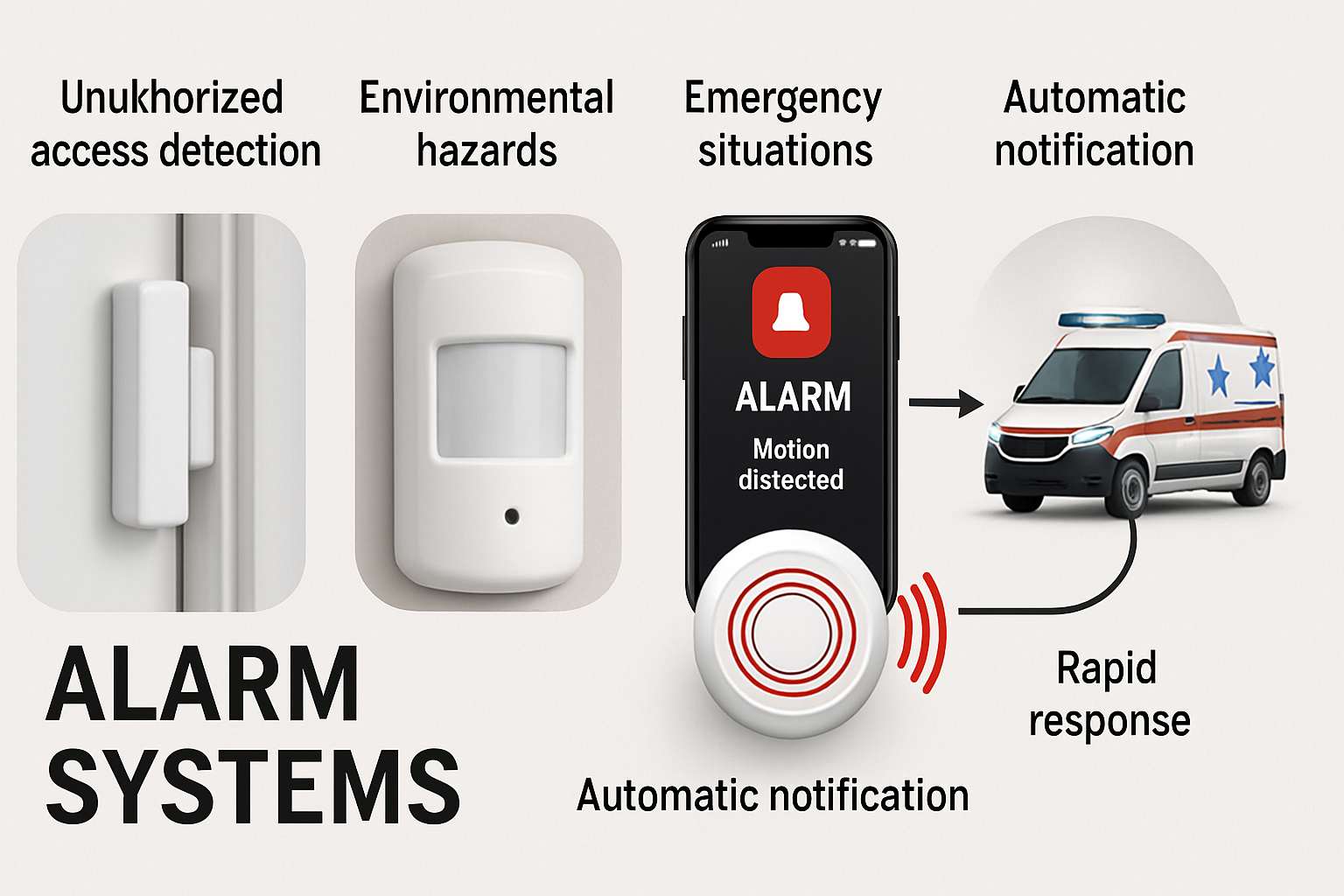
Alarm Systems
Alarms act like an immediate warning system. When there’s a break‑in, fire, or other emergency, the system triggers alerts so people can take action and help can be dispatched. Some alarms are loud to clear the area; others are silent to notify security.
- Follow alarm instructions immediately — don’t assume it’s a false alarm.
- Know your nearest exits and assembly points.
- Report accidental triggers or malfunctioning devices to security.
Video: Systems in Action
- Visual demonstration of each system type
- Real-world integration examples
- Employee interaction scenarios
Interactive Exercise
Security System Recognition (20 minutes)
Overview of a typical office facility showing how access control, CCTV, and alarm systems work together
You badge into the building and notice a security camera has rotated to focus on the entrance as you entered.
You notice that a card reader is making different sounds than usual and the LED is flashing red instead of green.
A visitor asks you to explain why there are so many different types of security systems in the building.
Module Assessment: Electronic Security Fundamentals
Answer all questions and select Submit. You need at least 75% to proceed to the next module.
Wrap-up
- Systems work together to protect your workplace.
- Your actions and adherence to procedures are critical.
- Report issues promptly; prioritize safety.
Coming Next: Module 2 — Access Control & CCTV Awareness.
Access Control & CCTV Awareness
A clear, hands-on overview of key cards, biometrics, and PIN code entry, along with how CCTV supports awareness and incident review.
Proximity cards communicate with readers; keep away from magnets/phones; present near reader—no swipe.
Use clean, dry hands; align as trained for consistent recognition.
Shield keypad; never share; report suspected compromises immediately.

Key Card Systems
A key card is an electronic key. You hold it near a door reader, the system checks if you’re allowed in, and the door unlocks if everything matches. Every use is recorded (who, when, where), and lost cards can be turned off so they no longer work.
- Hold your card flat and close to the reader — no swipe needed.
- A beep/light confirms the reader saw your card.
- If authorized, the lock clicks and the door opens briefly.
- Use only your own card — never share or loan it.
- Keep cards away from magnets/phones to avoid damage.
- Report lost or damaged cards immediately for deactivation.
- Try once more holding the card steady and centered.
- Check for a different colored light or error tone on the reader.
- If it still fails, visit security/reception for help — don’t tailgate.

Biometric Systems
Biometrics use something you are — like a fingerprint, face, palm, or iris — as your secure “key.” You present your enrolled biometric to the reader; the system compares it to your stored template and unlocks if it matches and you’re authorized.
- Place your finger/hand as shown, or align eyes/face as instructed.
- Hold steady until you see a confirmation light or hear a beep.
- If authorized, the door unlocks briefly — enter without delay.
- Keep hands clean and dry; remove gloves when required.
- Follow the device’s placement guide for consistent reads.
- Never enroll others or share your credentials.
- Try again, placing your finger/hand flat and steady; try another enrolled finger if available.
- Wipe moisture/dirt; avoid lotions immediately before use.
- Use the approved backup method or visit security — don’t tailgate.

PIN Code Entry
A PIN is a secret code that only you know. Enter it on the keypad; the system verifies the code and unlocks the door for a short time if you’re authorized.
- Wake the keypad if needed, then enter your PIN slowly and accurately.
- Watch for a green light or success tone, then open the door promptly.
- If you make a mistake, wait for the keypad to reset and try again.
- Shield the keypad with your hand while entering.
- Never share or write down your PIN; change it if compromised.
- Report suspicious behavior or keypad damage immediately.
- Re‑enter carefully; ensure the keypad isn’t locked out from rapid attempts.
- Look for error tones/lights and follow on‑screen prompts if present.
- Visit security for assistance — don’t prop doors or follow others in.
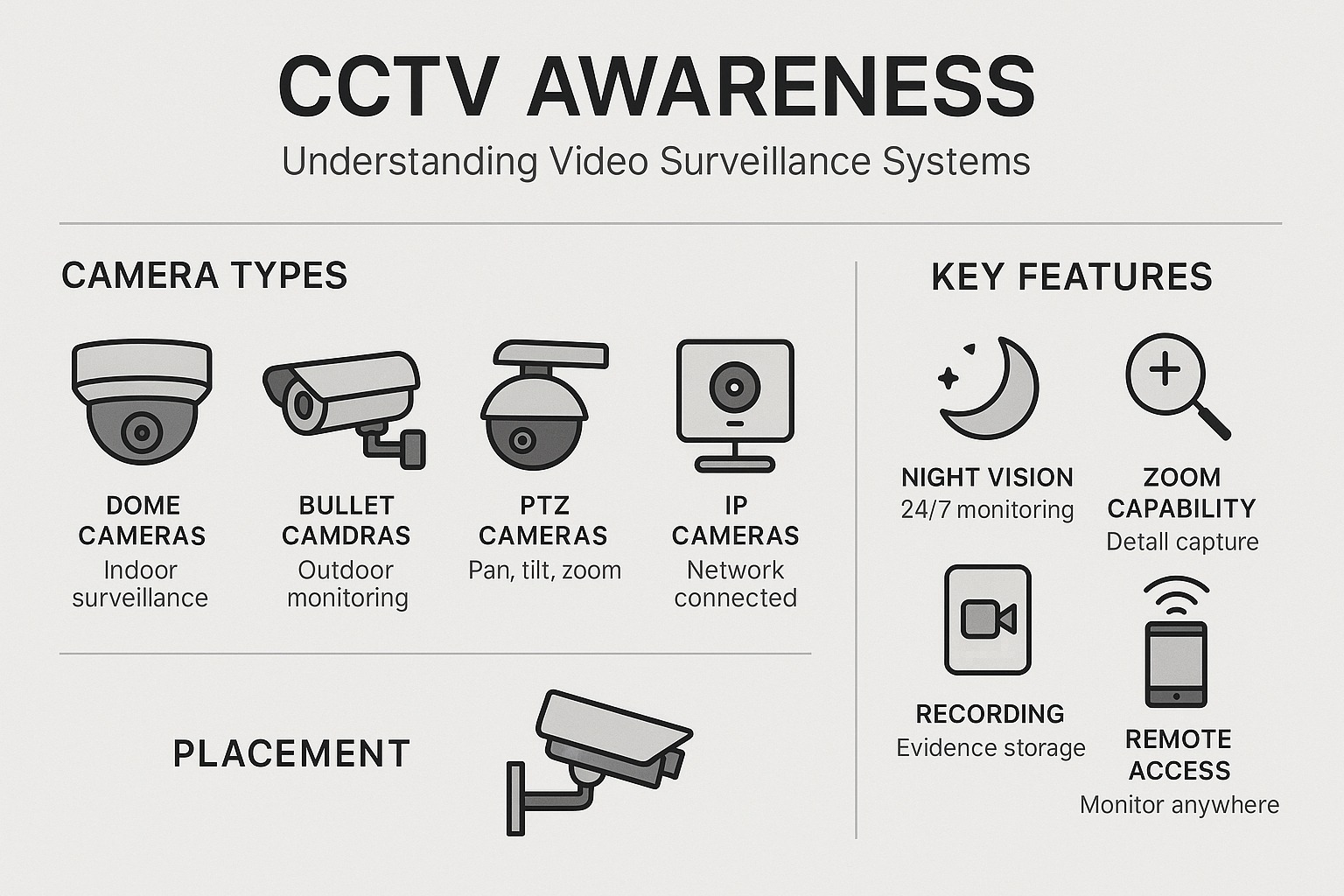
CCTV Awareness
CCTV helps keep shared spaces safe by providing visibility in entrances, lobbies, corridors, parking areas, and other common areas. It is not for private spaces. Footage can help understand incidents and improve safety.
- Deters unsafe or unauthorized behavior in common areas.
- Provides recorded evidence for incident review.
- Supports real-time awareness at key entry points.
- Don’t tamper with or block cameras.
- Report damage, obstruction, or unusual movement immediately.
- Be mindful of privacy: cameras do not monitor private areas.
- Call out obscured, mis-aimed, or non-functioning cameras.
- Report privacy concerns via HR or the designated channel.
- Do not attempt to reposition or repair cameras yourself.
Video: Proper Access Control Procedures
- Key card technique, biometric usage, and PIN security
- Anti-tailgating procedures
- Handling access denials
Best Practices & CCTV
Access Control
- Don’t loan credentials
- Don’t prop doors
- Ensure doors close/lock
- Prevent tailgating
CCTV Coverage & Privacy
- Entrances, lobbies, parking, corridors
- No cameras in private areas
- Footage stored securely
Interactive Exercise
Access Control Scenarios (18 minutes)
Exercise: "Make the Right Choice"
A colleague forgot their access card and asks you to let them into the secure area.
Your card isn't working on the reader, but the door seems loose.
A coworker mentions feeling uncomfortable about cameras in the break room.
Someone you don't recognize follows closely behind you as you enter a secure area.
Module Assessment: Access Control & CCTV
Answer all questions and select Submit. You need at least 75% to proceed to the next module.
Key Takeaways
- Follow proper access procedures; never compromise for convenience.
- CCTV balances security with privacy; know covered areas.
- Report issues immediately to maintain system integrity.
Alarm Systems & Emergency Procedures
Understand what each subsystem does and how to arm/disarm safely during daily operations and emergencies.
Detects unauthorized entry so alerts can be raised and responses activated.
- • Door/window contacts
- • Motion detectors
- • Glass break sensors
- • Perimeter detection
Silent alerts for genuine emergencies; never share or test duress codes without authorization.
Monitors hazards to protect people and assets.
- Fire
- Water
- Temperature
- Air quality
Prepare and activate the system safely before leaving.
- Verify areas are clear
- Close/lock points
- Enter code & confirm
- Confirm armed status
- Document issues
Enter safely and return systems to normal without false alarms.
- Enter within delay
- Go to panel immediately
- Enter code correctly
- Verify disarmed status
- Check alerts/issues

Intrusion Detection
In plain terms: intrusion detection is a set of sensors and controls that notice when someone or something enters where it shouldn’t, so we can act quickly and safely.
- • Door/Window Magnetic Contacts
- • Motion Detectors (PIR)
- • Glass Break Sensors
- • Vibration/Tilt Sensors (safes, equipment)
- • Perimeter Beams & Fence Sensors
- • Control Panel & Keypads (zones)
- Sensors watch doors, windows, rooms, or perimeters.
- When armed, a triggered sensor sends an alert to the panel.
- The panel signals an alarm locally and/or to monitoring.
- We follow procedures to verify and respond safely.
- • Know which zones you’re responsible for.
- • Arm/disarm correctly; use duress codes only for real threats.
- • Keep sensor areas clear (no blocked motion detectors).
- • Report damaged or faulty sensors immediately.
- Pause. Assess for signs of forced entry from a safe position.
- Follow escalation: notify monitoring/supervisor as required.
- Do not put yourself at risk; wait for backup if needed.
- Document what happened and actions taken.
- • Verify doors/windows latch fully before arming.
- • Keep moving objects and pets out of motion fields.
- • Enter/exit within delay times; know your code.
- • Report recurring false alarms for maintenance.
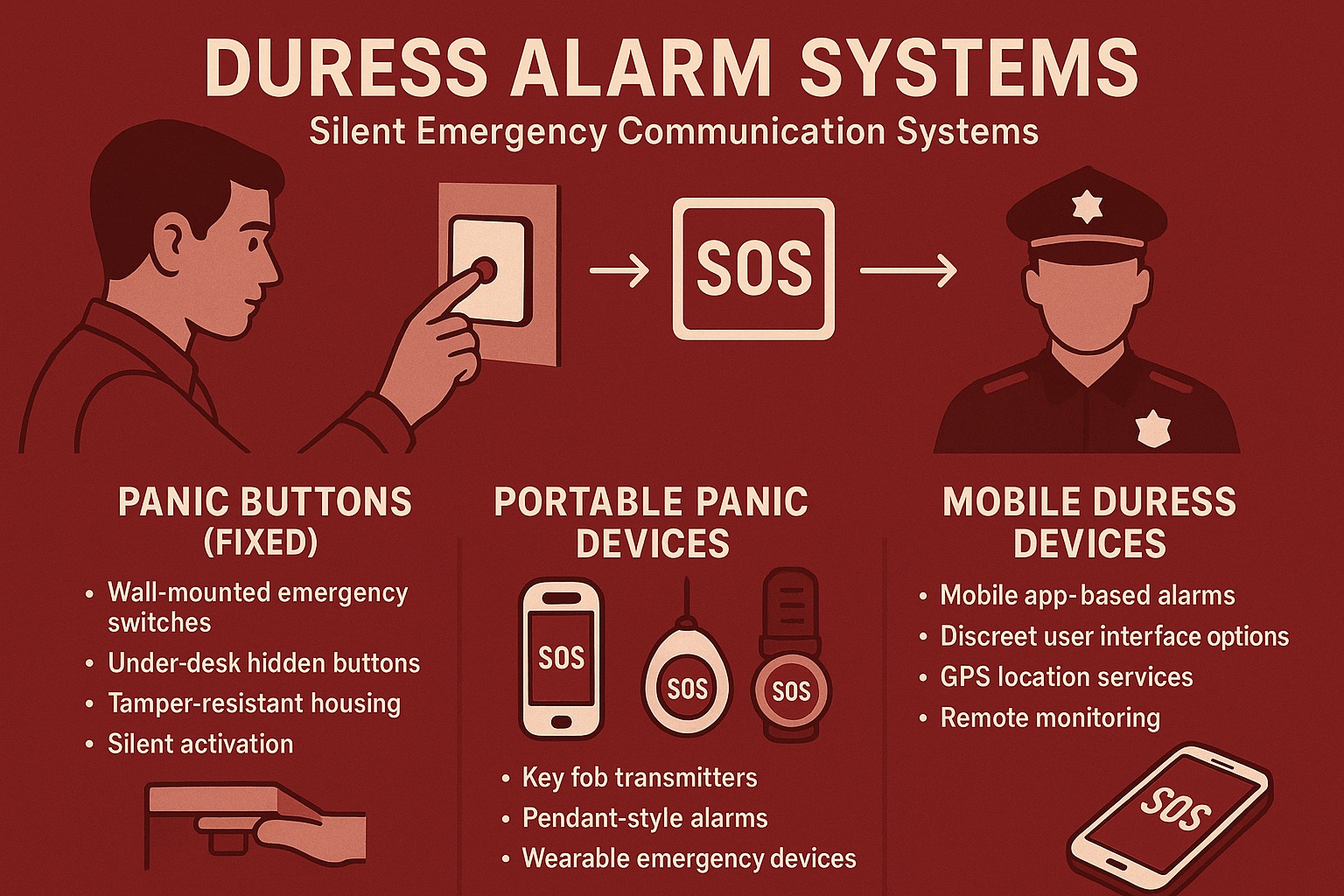
Duress Alarms
A duress alarm is a silent signal that tells security you’re being forced or threatened. It looks like a normal disarm but secretly sends an alert for help. Use it only in real emergencies.
- • Enter a special “duress code” or press a hidden button
- • The system appears to disarm normally
- • A silent alert goes to monitoring/security
- • Responders follow a preplanned protocol
- • Memorize your duress code; never write or share it
- • Use only if you’re under real threat
- • Do not test without explicit authorization
- • Afterward, cooperate with responders discreetly
- • Notify security immediately in person or by phone
- • Follow cancellation procedures if instructed
- • Expect a verification call/visit

Environmental Monitoring
These sensors watch for hazards like fire, smoke, water leaks, extreme temperatures, or poor air quality so people and property stay safe.
- • Fire/smoke and heat detectors
- • Water leak/flood sensors
- • Temperature and humidity
- • Air quality and gases (where applicable)
- • Don’t cover or block detectors
- • Report leaks, overheating, or persistent alarms
- • Follow evacuation instructions during fire alarms
- • Keep areas tidy to reduce risks
- • Treat alarms seriously; don’t assume false alarm
- • Evacuate or isolate area as directed
- • Inform security/facilities with location details

Arming Procedures
Arming prepares the site when leaving so sensors can protect the space.
- Verify people have exited and doors/windows are closed
- Secure any special zones (server/store rooms)
- Enter your code or present credential to arm
- Wait for confirmation (armed indicator)
- Report any faults before leaving
- • Leaving a door ajar causing a zone fault
- • Ignoring panel warnings or beeps
- • Rushing out during exit delay without checking status

Disarming Procedures
Disarming safely prevents false alarms and keeps you protected when entering.
- Enter within the delay time and go straight to the panel
- Enter your code accurately; avoid multiple rapid attempts
- Confirm “disarmed” and check for alerts
- • Pause and look for signs of intrusion from a safe spot
- • Follow escalation policy; don’t put yourself at risk
- • Document what happened and notify security
Visitor Management
Visitor management ensures only authorized guests enter and their presence is tracked for safety.
- • Register visitor details and verify ID
- • Issue a visible, time-bound badge
- • Log entry/exit and host responsibility
- • Escort visitors where policy requires
- • Retrieve badges at exit
- • Report suspicious behavior immediately
- • Only needed data is collected and stored securely
- • Integrates with access control for door permissions
Video: Alarm System Operations & Visitor Protocols
- Proper arming/disarming sequences
- Duress signal procedures (training scenario)
- Visitor check-in, escort responsibilities, evacuation
Interactive Exercise: Emergency Response Scenarios (20 minutes)
Exercise: "Critical Decision Making"
You arrive and the alarm is sounding. What's your priority?
A visitor seems nervous and can't clearly explain their business purpose.
Someone forces you to disarm the alarm system.
Module Assessment: Alarm Systems & Visitor Management
Answer all questions and select Submit. You need at least 75% to complete this module.
Resource Library
- Electronic Security System Quick Reference Card
- System Status Indicators Guide
- Troubleshooting Flowchart
- Access Control Best Practices Guide
- Key Card Care and Maintenance
- Biometric System User Guide
- PIN Code Security Guidelines
- CCTV Coverage Area Map
- Privacy Policy Summary
- Camera System FAQ
- Alarm Code Reference Card (secure storage)
- Arming/Disarming Procedure Checklist
- Zone Identification Guide
- Duress Procedure Summary (confidential)
- Visitor Management System User Guide
- Escort Procedure Guidelines
- Visitor Badge Types & Restrictions
- Emergency Visitor Protocols
- Emergency Contact Directory
- Evacuation Procedure Summary
- Incident Reporting Forms
- Security Emergency Response Guide
- Security Procedure Compliance Checklist
- Refresher Training Schedule
- Security Awareness Updates
- System Update Notifications
You've completed all three modules of the Basic System Awareness course. Keep practicing safe procedures daily to maintain a secure workplace.